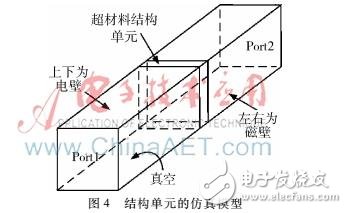
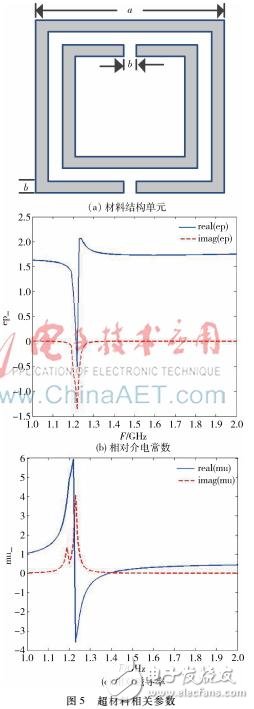
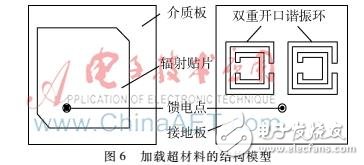
A single-frequency antenna operating at 1.575 GHz and a metamaterial structural unit exhibiting magnetic negative characteristics from 1.2 GHz to 1.4 GHz were designed. Loading two metamaterial structural units on the single-frequency antenna ground plane allows the antenna to operate at 1.268 GHz and 1.575 GHz. Among them, the higher resonant frequency is generated by the antenna itself, and the lower resonant frequency is generated by the addition of the metamaterial structural unit. The antenna has the characteristics of compact structure, frequency bandwidth, small size and easy processing. The single-frequency antenna is processed in kind, and the simulation results are basically consistent with the measured results. 0 Preface Satellite navigation system refers to a professional system that provides location, speed and other information services for various carriers on the ground, ocean, space and space. It can realize the positioning, navigation and management of targets, and has played an important role in different fields such as military and civilian. The role of becoming an indispensable radio application technology. Currently, Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) include GPS in the United States, GLONASS in Russia, Galileo in Europe, and BDS 1/2 in China. Among them, GPS and GLONASS have covered the world. The Beidou generation can provide navigation and communication services at the same time and has been successfully applied in China. In 2012, Beidou II officially provided services to most of Asia Pacific. With the development of multi-mode satellite integrated navigation technology, satellite receiving antennas that can receive multiple frequency signals have received extensive attention. The navigation satellite signal requires the navigation terminal antenna to have good right-hand circular polarization characteristics. In order to meet various needs, antennas with different performances such as broadband, multi-band, and miniaturization have become mainstream trends. The microstrip antenna has the characteristics of low profile, light weight, low cost and easy integration. With the development of technology, multi-band antennas have become a research hotspot. However, most antennas can only cover a single band. The proposed antenna can cover the GPS L1, GLONASS L1, BDS-2 B1 and B3 bands. However, the antenna is large in size, thick in thickness, and has a relatively complicated feed network. At the same time, the antenna design given in the literature considers the electrical performance of the antenna itself. The design of the structure and the requirements of different carriers are rarely considered, such as the size limit of the carrier of the antenna. Metamaterials are a class of equivalent homogeneous artificial composite structures (composites) with ultra-long physical properties not found in materials in nature. Metamaterials are composed of artificially constructed microstructures, and their overall electromagnetic properties are described by equivalent dielectric constant and equivalent permeability. For the convenience of introduction, the magnetic permeability is set to the abscissa and the dielectric constant is set to the ordinate. The theoretical space exists in the four quadrants according to the positive and negative relationship between magnetic permeability and dielectric constant, as shown in Fig. 1. Shown. 1 antenna design 1.1 Design of single frequency antenna The single-frequency antenna designed in this paper works in the 1.575 GHz (GPS L1) band, and the structural model is shown in Figure 2. The cut angle of the radiation patch is to achieve circularly polarized radiation, and adjusting the patch size can change the operating frequency of the antenna. The dielectric plate has a dielectric constant of 2.65, a thickness of 3 mm, a ground plate size of 76 mm & TImes; 76 mm, a patch size of 56 mm & TImes; 56 mm, and two isosceles triangles are cut diagonally at the patch. The waist of the isosceles triangle is 6 mm & TImes; 6 mm, fed by a 50 Ω coaxial cable with a feed point distance of 11 mm from the center. The analysis shows that the antenna simulation has a reflection coefficient of -15.03 dB, a bandwidth of 58.3 MHz, a physical reflection coefficient of -23.5 dB, and a bandwidth of 26.3 MHz. As shown in Figure 3, it can be seen from the pattern that the antenna is right-handed circularly polarized radiation. 1.2 Parameter extraction of metamaterial structural unit As shown in Fig. 4, the metamaterial structural unit is placed in the middle of the cuboid simulation area, the distance between the front and rear surfaces is equal to the port distance, the rest of the simulation area is vacuum, the upper and lower surfaces of the rectangular parallelepiped are set as electric wall boundary conditions, and the left and right surfaces are set as magnetic wall boundary conditions. . This boundary condition simulates the case where a TEM wave passes through a material sample. The plane wave is generated by the excitation of ports 1, 2, and the real and imaginary parts of the parameters S11 and S21 at ports 1 and 2 can be obtained by simulation. The data is imported into MATLAB, and the relative dielectric constant and relative magnetic of the metamaterial structural unit can be obtained. Conductivity. Wherein, the specific dimensions of the metamaterial structural unit in FIG. 5(a) are: a=15.24 mm; b=0.762 mm. As can be seen from the analysis in Fig. 5, the relative dielectric constant is positive and the relative magnetic permeability is negative in 1.2 GHz to 1.4 GHz. Therefore, it can be determined that this structural unit is a magnetically negative material. 1.3 Dual-frequency antenna loaded with metamaterials Two designed metamaterial structural units are loaded on the grounding plate of the single-frequency antenna, and the antenna structure is shown in FIG. 6. The distance of the structural element from the horizontal axis is 1 mm and the distance from the longitudinal axis is 1.27 mm. The antenna uses a single-feed feed to generate a frequency. Another frequency is then generated using the interaction between the metamaterial structural units. 2 antenna simulation analysis
OEM Laptop Ram manufacturer Memoria Ram ddr 4 4g 2666 memory sodimm 4gb ddr4 2666mhz dual channel RAM for laptop 16c PC4 21300 1Rx8
• 240-pin, unbuffered dual in-line memory module (UDIMM)
Ddr4 Desktop Memory,Ddr3 4Gb 1600Mhz,Ddr3 4Gb Ram Game Memory,Ddr3 8Gb Desktop Memory MICROBITS TECHNOLOGY LIMITED , https://www.hkmicrobits.com

A single-frequency antenna design working at 1.575 GHz
• VDD = VDDQ = 1.35V (1.283–1.45V)
• Fast data transfer rates: PC3-14900, PC3-12800, or PC3-10600
• 4GB , 8GB
• Nominal and dynamic on-die termination (ODT) for data, strobe, and mask signals
• Backward-compatible to VDD = VDDQ = 1.5V ± 0.75V
• VDDSPD = 3.0–3.6V
• Reset pin for improved system stability
• Dual-rank
• Adjustable data-output drive strength
• Fixed burst chop (BC) of 4 and burst length (BL) of 8 via the mode register set (MRS)
• Serial presence-detect (SPD) EEPROM
• Gold edge contacts
• Halogen-free
• Addresses are mirrored for second rank