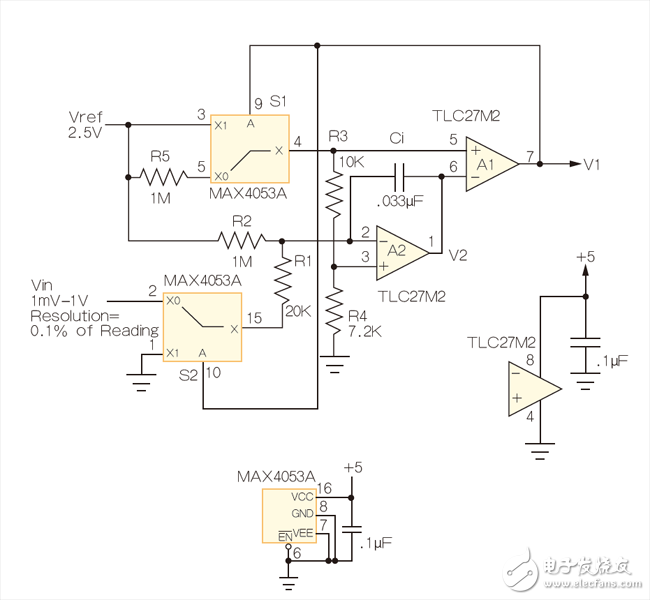
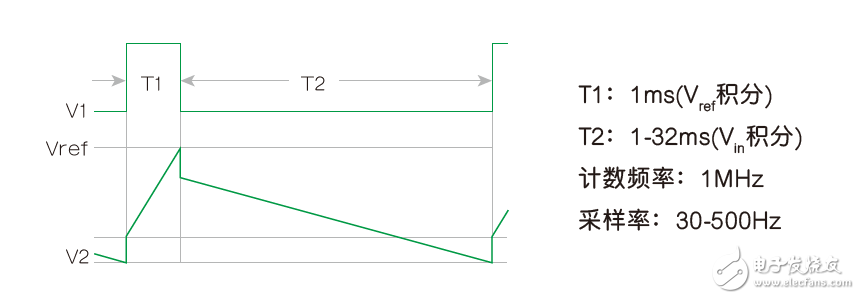
For four decades, double-slope integration A/D conversion has become the core of most digital multimeters and many industrial and instrumentation applications. The dual-slope analog-to-digital converter combines an analog integrator, comparator, and control logic to accumulate (integrate) the input signal Vin at a fixed time interval T1 - forming the first "slope" and then switching the input of the integrator To a fixed negative reference Vref, the integrand is returned to zero—the second “slopeâ€, and the time T2 required to do so is measured. The input voltage is: This design has made some modifications to common algorithms: simply inverting the order of the signal and reference integration, producing what I call the reciprocal double-slope integration ADC (RDSADC). Here, Vref is integrated at a fixed time interval T1. Then switch the integrator input to -Vin and measure the time T2 required to fall back to zero. thereby: Seeing these two similar equations, you may of course ask: "What about that?" Look at the following: In Equation 2, the conversion result is inversely proportional to the time measured value T2, and therefore is inversely proportional to 1/Vin, and the differential calculation tells us that the reverse change rate is changing, but it is not linear, but the square of the inverse of the measured value, that is: The benefit of this design is that a non-linear conversion measurement is achieved that maintains the high resolution of the low-amplitude input without the need for auto range switching of the Vin proportionality factor. Figure 1 is an implementation example of an RDS ADC. It converts the input in 10-bit resolution, 1mV to 1V range, while maintaining 10-bit resolution in the following two extreme cases: Vin = 1V, 1mV resolution; Vin = 1mV, 1μV resolution. This means that for T2, only 15-bit, 32k-count resolutions are needed to achieve 1,000,000:1, 20-bit dynamic range. In other words, as long as 15 bit counts can achieve 20-bit dynamic range, conversion time efficiency is 32 times faster than conventional DSADCs with similar resolution. In fact, Vin can go from 0V to 5V (the resolution is reduced). Figure 1: The RDSADC reverses the usual integration sequence to dramatically increase the dynamic range. How it works: The RDSADC cycle begins with S1 connecting the Vref to the “+†input of the integrator A2 (pin 3) via an R4/(R3 + R4) divider and integrating during the time interval T1 and ending when V2 = Vref, and Switch comparator A1 output low. Figure 2: RDSADC timing diagram. S1 lets A2's "+" input fall close to the reference ground (later lower), while S2 switches A2's "-" input closer to Vin via R1. V2 then falls with a slope that is almost proportional to Vin to determine the counting interval T2. When V2 reaches the low threshold of A1, T2 is terminated, the ADC cycle is completed and the next cycle is started, and the cycle continues. The astute reader will notice that during S2, when S1 removes Vref from A1's “+†input, R5 produces a positive bias of 42mV. The purpose of this bias is to maintain the output of A2 up to the end of the T2 ramp, despite the use of unipolar power supplies. Also during T2, R2 also produces a valid 32mV offset 1 to ensure that T2 stays finite for a period of time (never more than 32ms), even if Vin is near zero. thereby: This idealized calculation ignores real-world deviations such as A1 and A2 input offsets, Vref accuracy, and resistance changes, but these deficiencies can be easily compensated in a computational way with simple Vfullscale and Vzero two-point calibrations. Note 1: The 32mV is divided from R1-R2 to a 2.5V Vref (50mV), which provides 1.6μA (32mV/20kΩ) bias current for the Vin/20kΩ input current, minus the voltage divider R3-R5 (18mV The "keep-alive" bias provided. Therefore, 50mV - 18mV = 32mV. The so-called mini projector is also called pico projector, TRT-Lcos Portable Projector. Mainly through the 3M LCOS RGB three-color projector and 720P film decoding technology, the traditional huge projector is refined, portable, miniaturized, entertaining and practical, making the projection technology closer to life and entertainment. best mini projectors under £100,mini projector pvo portable projector,mini projector portable,mini projector amazon,mini projectors for movies Shenzhen Happybate Trading Co.,LTD , https://www.happybateprojectors.com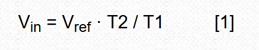
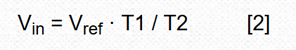
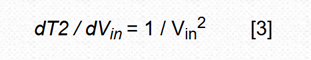
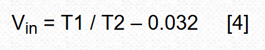
Usually the projector has certain regulations on 2 aspects:
a). Size: Usually the size is the size of a mobile phone.
b). Battery life: It is required to have at least 1-2 hours or more of battery life when it is not connected to power.
In addition, its general weight will not exceed 0.2Kg, and some do not even need fan cooling or ultra-small silent fan cooling. It can be carried with you (it can be put into your pocket), and the screen can be projected to 40-50 inches or more.
Advantage:
1. Completely replace the MP5 player, video, listening to songs, playing games, e-books, picture browsing, etc. MP5 video is affected by physical performance, the screen can not be bigger, and the screen of this thing is at least 20 inches.
2. Instead of the TV function, the machine can have a built-in CMMB function, or it can be directly connected to the set-top box to play the TV, and it can be used as a 21-inch TV during the day.
Look, it can be used as a 60-100-inch TV at night to achieve the effect of home theater; it is convenient to move and break through the traditional film and television space. Even if you are on the mountain, you can also share today's TV series, movies, and MTV with your lover.
3. Business office: instead of large projectors, it is used for company meetings; the price of large projectors is 4,000 to 14,000, and the lamp life is more than 1,000 hours, which is not convenient to carry. 30,000 hours, no need to change the bulb for 3 years, easy to carry, the salesman only needs to bring a micro projector to demonstrate the new product, which can achieve the demonstration effect.
4. Teaching: training meetings, classroom teaching; traditional projectors are not easy to carry. In school classrooms, due to the naughty students, projectors are not safe to place in the classroom and are easily damaged by students. The portability of micro projectors makes up for the teaching vacancies. In the future, teachers only need to store the materials in the projector and show them to students for teaching, saving the trouble of textbooks and handwriting with pens and chalks.
In addition, the micro-projection has no radiation, which can fully protect pregnant women and people with myopia. Its low power consumption function is 1/1,000,000 of the power consumption of color TVs. One day of electricity has completely impacted the indicators of safety, environmental protection, health, etc., and has made amazing contributions to future social development, standing at the peak of the green world as a leader.